- Home
- About
- Products
- Contact Temperature Sensors
- Cables & Wires
- Mineral Insulated Cables
- Nickel & Thermocouple Alloy
- Industrial Heaters
- Heating Cables and Mats
- Non Contact Temperature Sensors
- Industrial and R&D Furnaces
- Temperature Calibrators
-
Circulating Chiller
- Services
-
Special Products
- Thermal Profiling System
- Industries
- Resources
- Contact Us
- Shop
Comprehensive Guide to Temperature Gauges: Types, Features, and Usage

Temperature gauges play a crucial role in various industries, offering invaluable insights into thermal conditions for optimal performance and safety. In this blog post, we'll delve into the fundamentals of temperature gauges, exploring what they are, the different types available, their applications across industries, and a special mention of Tempsens – a leader with over 45 years of experience in providing cutting-edge thermal and cable solutions.
What is a Temperature Gauge ?
A temperature gauge is a device designed to measure and display the temperature of a particular system or environment. Whether in automotive, industrial, or scientific settings, these instruments help ensure that processes are running within safe and efficient temperature ranges.
Types of temperature gauges:
- Bimetallic Temperature Gauges: Bimetallic temperature gauges operate on the principle of the expansion and contractionof two metals with different coefficients of thermalexpansion. As temperature changes, the metals bend, causing a pointer to move across a scale.

-
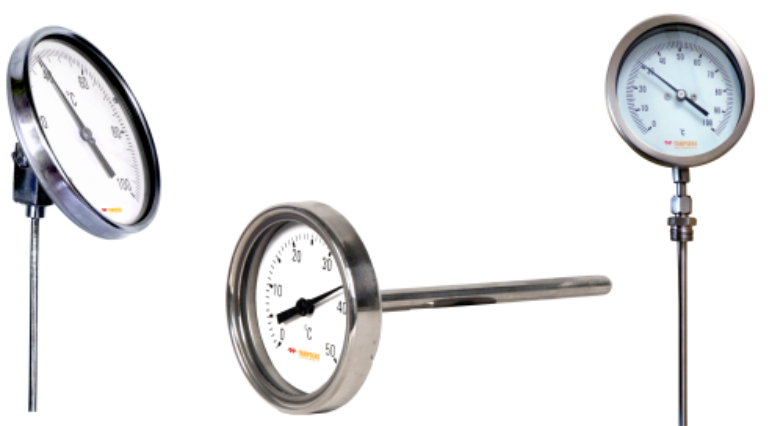
Liquid Filled Thermometer: This traditional type of temperature gauge consists of a glass tube containing a liquid filled with Glycerin/Silicon Oil.It expands or contracts with temperature changes. The level of the liquid corresponds to the temperature on a calibrated scale. It is used where mercury thermometers cannot be used.
- Gas (Expansion) Thermometers: Gas thermometers use the change in pressure or volume of a gas to measure temperature. This type is often used in scientific applications where high accuracy is crucial.
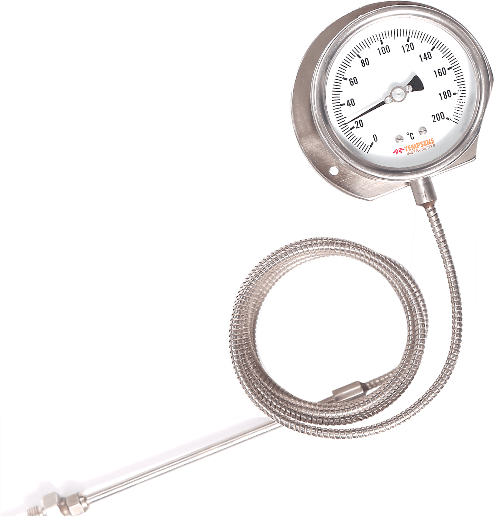

Features of Temperature Gauges
Temperature gauges come with various features that cater to different applications and requirements. The features of temperature gauges contribute to their accuracy, reliability, and adaptability. Here are some common features associated with temperature gauges:
- Temperature gauges are crafted to measure specific temperature ranges, making them adaptable to a variety of applications.
- Precision is crucial, especially in industries requiring exact temperature control, where high-precision gauges offer reliable readings.
- Response time matters, particularly in applications with rapid temperature changes, allowing for timely adjustments.
- Durability features like rugged construction and resistance to corrosion enhance gauges' reliability in harsh industrial environments.
- Various mounting options, display types, scale and unit customizability, and connection types provide flexibility for different installations and user preferences.
- Some gauges include alarm features for critical temperature thresholds.
- Calibration options are available for precise temperature readings, and advanced gauges may offer remote monitoring for real-time data access.
- Ingress Protection (IP) ratings indicate protection levels against dust and water, making higher ratings suitable for environments with moisture or dust concerns.
Applications of Temperature Gauges
Temperature gauges find extensive applications across various industries due to their crucial role in monitoring and controlling temperature conditions. Here are some notable applications of temperature gauges:
-
- Manufacturing and Processing Industries : Control material temperature during production for optimal quality and efficiency.
- HVAC Systems: Regulate indoor climate conditions in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings for comfort and energy efficiency.
- Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals: Maintain correct storage conditions for medications and sensitive materials in laboratories and healthcare facilities.
- Food and Beverage Industry : Monitor cooking, refrigeration, and fermentation processes for food safety and compliance.
- Energy Production and Power Plants: Monitor operating temperatures of components in power generation facilities for efficient and safe operation.
- Automotive Industry: Integrated into vehicles to monitor engine temperature, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
- Aerospace and Defense: Monitor thermal conditions of critical components in aerospace applications for safety and reliability.
- Environmental Monitoring: Track temperature variations in ecosystems, bodies of water, and climate research for understanding climate change.
- Plastics and Rubber Industry: Control temperature during molding, extrusion, and curing processes for desired material properties.
- Oil and Gas Industry : Monitor temperatures in drilling, refining, and transportation processes for safety and efficiency.
- Electronics and Semiconductor Manufacturing: Ensure precision temperature control for reliability and performance of electronic components in manufacturing
Thus as concluded, Temperature Gauges are indispensable tools for maintaining control and ensuring safety in various applications. The right choice of temperature gauge depends on the specific requirements of the industry or process.
Tempsens Leading Thermal and Cable Solutions: With over 45 years of expertise, Tempsens has been at the forefront of providing innovative thermal and cable solutions. Specializing in temperature measurement, Tempsens offers a diverse range of products, including thermocouples, RTDs (Resistance Temperature Detectors), Gauges and temperature sensors. Their commitment to quality and innovation has made them a trusted partner in industries worldwide.
In the dynamic landscape of temperature measurement, Tempsens continues to lead, providing solutions that meet the evolving needs of industries and ensuring precision and reliability in temperature monitoring.
Explore the world of temperature gauges with Tempsens, where experience meets innovation for 45+ years!
FAQ
What is the importance of a temperature gauge?
A temperature gauge is a device used for the accurate measurement and reading of temperature gradient. The term temperature gauge usually, though not always, refers to a device showing readings on a numbered dial. Dial thermometer gauges are often found in industrial and commercial settings.
What makes the temperature gauge work?
The tip of the sensor has a spring that is attached to a rod, leading up to the gauge needle. The spring sits inside the stems sensing end. When heat is applied to the sensing coil, movement in the coil is created which causes the needle in the gauge to move – thus displaying the temperature.
What are the 6 uses of thermometer?
- It indicates temperature deviation.
- It can be used to measure the temperature for air.
- It is both used in Centigrade and Fahrenheit.
- It can also note the maximum temperature.
- It intimates the highest and lowest temperature.
- It is measuring the temperature for preparing weather reports.
For details visit at https://tempsens.com/catalog/contact-temperature-sensors/guages/temperature-gauge.html